Table of Contents
BEST IELTS General Reading Test 513
IELTS GENERAL READING TEST 513 – PASSAGE – 3

IELTS GENERAL READING TEST – 513
READING PASSAGE – 3
What they’re doing to our bread!
Most people agree that wholemeal bread is better for us than white bread but, with increasing levels of gluten sensitivity, a few consumers steer clear of wheat bread altogether. However, for the majority of us who enjoy a slice of toast in the morning and don’t seem to suffer any ill effects, is there any real cause for concern?
The problem lies in how commercial flour and bread production has changed over time. Bread technology has advanced to a point where bread still looks like bread, but has lost a degree of the integrity it had in a pre-industrialised era. In the 1950s and 60s, the wheat industry was transformed in what was known as the Green Revolution. Different varieties of wheat were produced, primarily to deliver higher yields which were also more resistant to harsh climatic conditions.
IELTS General Reading Test
The new wheat strains, combined with the introduction of pesticides, significantly improved the annual harvest. However, the wheat that we now eat bears little resemblance to the ancient varieties reaped and eaten for thousands of years. Questions must be raised over the impact of the new wheat on our health. Is it wise to consume bread made from mutated wheat grown with chemicals, excessively refined and then pumped up with artificial additives?
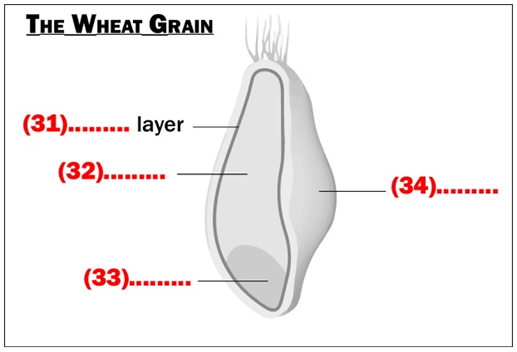
A wheat grain is usually oval shaped with several layers of bran on the outside to protect the seed. This is generally not included in flour because of its colour and texture. At one end of the grain is the germ, which is also not wanted because of its high fat content, which reduces shelf life. Most of the interior is made up of the highly desired whitish endosperm, the main constituent of flour. There is a thin layer between the outer shell and the inside called aluerone which is a rich source of essential vitamins. Unfortunately, in the milling of white flour these are lost and are later replaced by synthetic vitamins.
IELTS General Reading Test
The milling process breaks open the grain, which is then ground into flour by being repeatedly rolled and sieved. During this process, the flour that is generated is separated into up to 16 flour streams – the bran into one, the germ into another, and varying degrees of refined white flour into other streams. The grade of wheat flour is defined by the extraction rate.
Very fine white flour, for example, is made from the inner third of the grain only, and is called a 33% extraction flour. Straight run flour, which has a 100% extraction rate, is a combination of all the flour streams – in other words, it is made up of flour from the entire wheat grain, including the bran, germ and endosperm.
Whole wheat flour naturally contains much higher quantities of fibre, B vitamins and minerals than white flour, due to its bran and germ content. It is for this reason that wholemeal bread is perceived as ‘good’ and white bread as ‘bad’. In some countries, the extraction rate for white bread is less than 75%, whereas in others which use smaller scale milling processes, this can rise to 78%.
This means that higher levels of nutrients are retained and it does not need enriching with synthetic vitamins and minerals as occurs in countries where flour production processes are more industrialised. In the US, it is permitted to bleach flour with chlorine dioxide to make it whiter, but in other countries this bleaching is prohibited.
IELTS General Reading Test
In some countries, bread manufacturers add hydrogenated fats to expand the volume, enhance the crumb texture and prevent staling. Perhaps a more controversial addition to bread is improver, also known as flour agent or dough conditioner. An improver is a mix of various acids and enzymes that strengthens the gluten and speeds up the dough development process.
Improvers typically contain added gluten, which helps produce a fluffier, lighter loaf – and which is also associated with an increase in gluten intolerance. Emulsifiers are also typically added to improvers to control the size of gas bubbles in the dough, which allows it to hold more gas and therefore grow bigger, resulting in bread with a softer crumb and a reduced staling rate.
IELTS General Reading Test
Fortunately for health-conscious bread lovers, in most countries there is an alternative to commercially-produced wheat bread. Consumers may choose to purchase bread from small scale, local bakeries that guarantee a higher quality product, although this is generally more expensive than the mass-produced alternatives. Many of these products have lower yeast content, and some use ancient varieties of grain such as spelt or khorasan. There are even benchtop stone mills now that allow eager home bakers to grind their own flour, ensuring maximum retention of nutrients from premium quality grain.
Questions 28–30
Choose NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS from the text for each answer.
28. What causes some people to avoid eating bread?
29. What was the first reason for introducing new types of wheat?
30. What also helped to increase the production of wheat?
IELTS General Reading Test
Questions 31–34
Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the text for each answer.
IELTS General Reading Test
Questions 35–40
Choose NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS from the text for each answer.
The milling of flour and production of bread
· wheat grain is ground, rolled, sifted
· various 35……………….. produced: bran, germ, different grades of refined white flour
· very fine white flour = 33% extraction
· 36……………….. = 100% extraction (uses the whole grain)
· whole wheat flour has more fibre, B-vitamins & minerals than white flour
· large-scale production = <75% extraction
· smaller-scale production = up to 78% extraction
· greater extraction means not necessary to add 37……………….. nutrients
· in US, flour may be bleached
· fat may be added to make larger loaves which last longer & to improve 38………………..
· improvers (with extra gluten) make lighter loaves
· 39……………….. increase the amount of gas so dough expands
· local bakeries produce higher priced but better quality bread with 40……………….. & ancient grains
· home bakers can use benchtop mills to produce wholesome bread
IELTS General Reading Test

IELTS General Reading Test
ANSWERS
28. GLUTEN SENSITIVITY
29. (DELIVER) HIGHER YIELDS
30. (INTRODUCTION OF) PESTICIDES
31. ALUERONE
32. ENDOSPERM
33. GERM
34. BRAN
35. (FLOUR) STREAMS
36. STRAIGHT RUN FLOUR
37. SYNTHETIC
38. (THE) CRUMB TEXTURE
39. EMULSIFIERS
40. LOWER YEAST CONTENT
IELTS General Reading Test