Table of Contents
BEST IELTS Academic Reading Test 496
IELTS ACADEMIC READING TEST 496 – PASSAGE – 1

IELTS ACADEMIC READING TEST – 496
READING PASSAGE – 1
Are Feathers Just for Flying?
More uses than you might think
The feathers on a bird serve a multitude of purposes from flying, attracting a mate to protecting it from the cold. Basically, feathers are what distinguish birds from other animals and even though much research has gone into understanding their mechanism, much about them is still very mysterious. By using hi-tech tools, such as electron microscopes and high-speed video, it has been revealed that feathers are multitaskers, performing numerous functions simultaneously. They function as flight equipment, rain protection and courting clothes for birds. They are a measure of how a bird has been living, what it has been eating.
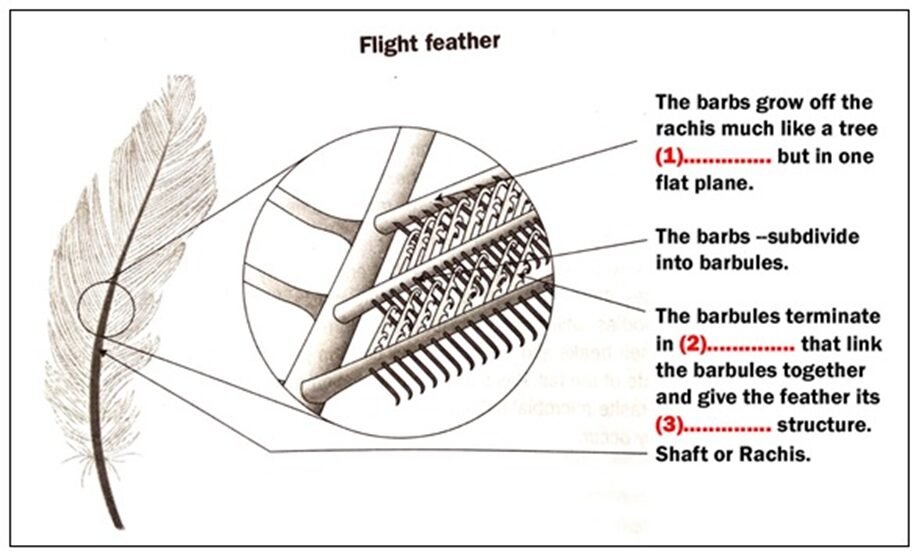
Feathers develop in much the same way as human hairs – dead keratin growing out through a skin follicle. However, it is a much more complex process. A feather is structured somewhat like a tree. The hollow shaft or rachis grows numerous branches, called barbs. In tail and wing feathers the barbs are further subdivided into barbules.
On flight feathers the barbs all grow on one flat plane and the barbules link to the barbules on the adjacent barb by hooklets on the end of each barbule. This structure forms a smooth stiff surface that creates a durable aerodynamic form. On feathers of the belly, called down feathers, the barbs go in many different directions to trap air and provide insulation. Down feathers are the ones used in pillows and bedcovers.
IELTS Academic Reading Test
The fossil record contains a host of well-preserved feathers from dinosaurs and ancient birds. As these feathers are almost identical to the feathers on birds today, palaeontologists are unable to explain how feathers originally evolved. In recent years some fossil bird feathers were discovered in rock deposits in Germany. Under an electron microscope the surface of the feathers was covered in a substance that looked like crushed carpet, in tightly packed cylindrical blobs. At first it was thought that they were bacterial cells, but they were in fact melansomes in feather cells.
A melansome is an organelle in the cell that contains dark pigment and its presence indicates the fossil birds were probably a dark colour with iridescent highlights, like a blackbird today. Since then a number of other fossils have had their colours reconstructed using this process and it seems that feathered dinosaurs from 150 million years ago sported some very bright colours, as many birds still do today. Most feather colours, such as reds, oranges and yellows, result from pigments.
IELTS Academic Reading Test
Blues come from intricate protein structures that reflect light in a certain way, and greens are produced by both pigment and light-reflecting proteins. As well as through pigments, birds can change the colour of their feathers through nanostructures, which reflect the light in different ways. Iridescent feathers, like on peacocks, possess those which fracture the light much like the formation of a rainbow.
Some feathers, like the pink of the flamingo, are the direct result of the food it eats. Flamingos consume crustaceans that contain coloured proteins. The flamingo’s digestive enzymes turn these proteins into new pigments which are then deposited into the feathers. Flamingos in captivity require a special diet enriched in chemical pigment to ensure they preserve their striking colours. The best explanation for the development of different coloured feathers is for mating and reproduction.
IELTS Academic Reading Test
It has been shown that in many bird species with pigmented colouration, such as yellows, reds and oranges, the more brightly coloured male is the preferred mate for females. The pink colour of flamingos is heightened during the mating period. As they are not migratory birds so their diet does not change, their colour should remain the same.
This increase in pigmentation occurs due to a pink, pigmented oil that they produce in their preen gland, which is a small organ beneath the tail. The birds preen themselves by rubbing themselves with their bills and heads and transfer more colour onto their feathers. They do this primarily during the mating season and it has the effect of making them more attractive to potential mates.
IELTS Academic Reading Test
Studies of North American barn swallows have shown that females prefer males with darker breast feathers. By artificially intensifying the colour of the breast feathers, scientists have found that they breed earlier and father younger. But it seems that there is another factor at play. The birds with experimentally altered feather colour also experienced a surge in the sex hormone testosterone.
Thus it seems a bird’s external appearance can change its internal hormone levels. The information that the appearance of the feathers provides, not only speaks to mates but to the bird itself. Scientists believe this raised testosterone occurs through the social feedback they receive from the way potential mates react to different intensities of feather colour.
IELTS Academic Reading Test
Preening is the process by which birds clean their feathers. It is done to clear them of dirt and parasites and make sure the feathers themselves have a regular form that ensures they are safe for flight and still have water resistance. It also makes them more attractive to future mates. When birds preen they are able to reach every feather on their bodies, which accounts for the contorted positions that birds are often seen in.
They preen themselves with their beaks and feet which they cover in preen oil, produced by the preen gland which is found on the underside of the tail. Preen oil is a combination of waxes and oils and in many species of birds also contains anti-parasite microbial substances. Regular preening is required for optimal health or feather loss and baldness may occur.
IELTS Academic Reading Test
Questions 1-3
Choose NO MORE THAN ONE WORD from the passage for each answer 1-3.
IELTS Academic Reading Test
Questions 4-8
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
TRUE – if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE – if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN – if there is no information on this
4. Feathers can tell us how intelligent a bird is.
5. The development of feathers is shown in the fossil record.
6. The colours of ancient birds were identified by observing bacterial cells in fossil feathers.
7. Blue colours in feathers are not the result of pigments.
8. Iridescence on a feather is more a trick of light than a colour.
IELTS Academic Reading Test
Questions 9-13
Choose NO MORE THAN ONE WORD from the passage for each answer.
FLAMINGOS
– Flamingos are pink because of a crustacean they eat that contains pink-coloured proteins.
– Flamingos in zoos need to be given artificial 9………………… in order to produce pink feathers.
– In the wild they can increase the intensity of their colour by using a pink-coloured 10………………… produced by a particular gland under their tail.
IELTS Academic Reading Test
BARN SWALLOWS
– Found that females prefer males with darker breast feathers.
– Changing the feather colour in male birds can affect 11………………… production, particularly testosterone.
– It happens because of the positive feedback they get from females.
PARROTS
– Birds that live in the tropics can have feathers with an 12………………… effect..
PREENING
– Birds clean every feather on their body with a process called preening. They need to do this to stay in good 13…………………
IELTS Academic Reading Test

IELTS Academic Reading Test
ANSWERS
1. BRANCHES
2. HOOKLETS
3. AERODYNAMIC
4. NOT GIVEN
5. FALSE
6. FALSE
7. TRUE
8. TRUE
9. PIGMENT
10. OIL
11. HORMONE
12. ANTIBACTERIAL
13. HEALTH
IELTS Academic Reading Test